Who Should Get Screened for Diabetes? Risk Factors You Need to Know
Diabetes is a growing health concern worldwide, and early detection plays a crucial role in preventing its complications. Many individuals remain uncertain about their risk level and whether testing is necessary. Knowing the risk factors helps you understand when diabetes screening is an essential healthcare step. This guide outlines who should consider screening, the types of tests available, and the importance of early diagnosis.
Why Screening for Diabetes Is Crucial
Diabetes is a condition where the body either doesn’t produce enough insulin or cannot effectively use it, leading to high blood sugar levels. Left untreated, diabetes can cause serious health complications, including heart disease, kidney damage, nerve problems, and vision loss. Early detection through regular screening can prevent or delay these outcomes by enabling timely treatment and lifestyle changes.
There are two main types of diabetes:
Type 1 Diabetes: An autoimmune condition usually diagnosed in childhood or early adulthood.
Type 2 Diabetes: A more common type linked to lifestyle and genetic factors, often developing in adults but increasingly seen in younger individuals.
Screening is particularly important because Type 2 diabetes often develops slowly and may not show symptoms until significant damage has occurred.

Who Should Get Screened for Diabetes?
Not everyone needs regular diabetes screening, but certain groups are at higher risk. If you fall into any of the following categories, it’s time to discuss testing with your healthcare provider.
1. People with a Family History of Diabetes
If you have a close relative, such as a parent or sibling, with diabetes, your risk increases significantly. Genetics plays a crucial role, particularly for Type 2 diabetes.
2. Individuals Aged 40 and Over
Age is a significant risk factor for Type 2 diabetes. Adults over 40, especially those with other risk factors, should consider regular screening. For South Asian, Black, or Chinese populations, the recommended age for screening drops to 25, as these groups are at a higher risk.
3. People who are Overweight or Obese
Excess weight, particularly around the abdomen, is a strong predictor of insulin resistance and Type 2 diabetes. If your BMI is 25 or higher (23 for some ethnic groups), talk to your doctor about a test.
4. Women with Gestational Diabetes
Women who develop diabetes during pregnancy (gestational diabetes) are more likely to develop Type 2 diabetes later in life. Regular screening post-pregnancy is essential for this group.
5. Those with High Blood Pressure or Cholesterol
Hypertension and abnormal cholesterol levels are closely linked to diabetes. If you’re managing either of these conditions, screening for diabetes should be part of your regular health checks.
6. Individuals with Pre-Diabetes
Pre-diabetes is a condition where blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not yet high enough to be classified as diabetes. If diagnosed, regular screening is vital to monitor progress and prevent the onset of full-blown diabetes.
7. Sedentary Individuals
A lack of physical activity can increase the risk of insulin resistance and diabetes. If you lead a sedentary lifestyle, consider a diabetes screening to assess your health.
8. People with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
PCOS affects hormonal balance and is often linked with insulin resistance, making women with this condition more vulnerable to Type 2 diabetes.
9. Individuals with Unexplained Symptoms
Certain symptoms might indicate undiagnosed diabetes, including:
-
- – Excessive thirst or urination
- – Persistent fatigue
- – Blurred vision
- – Slow-healing wounds
- – Unexplained weight loss (for Type 1 diabetes)
If you notice these signs, it’s essential to undergo a test.
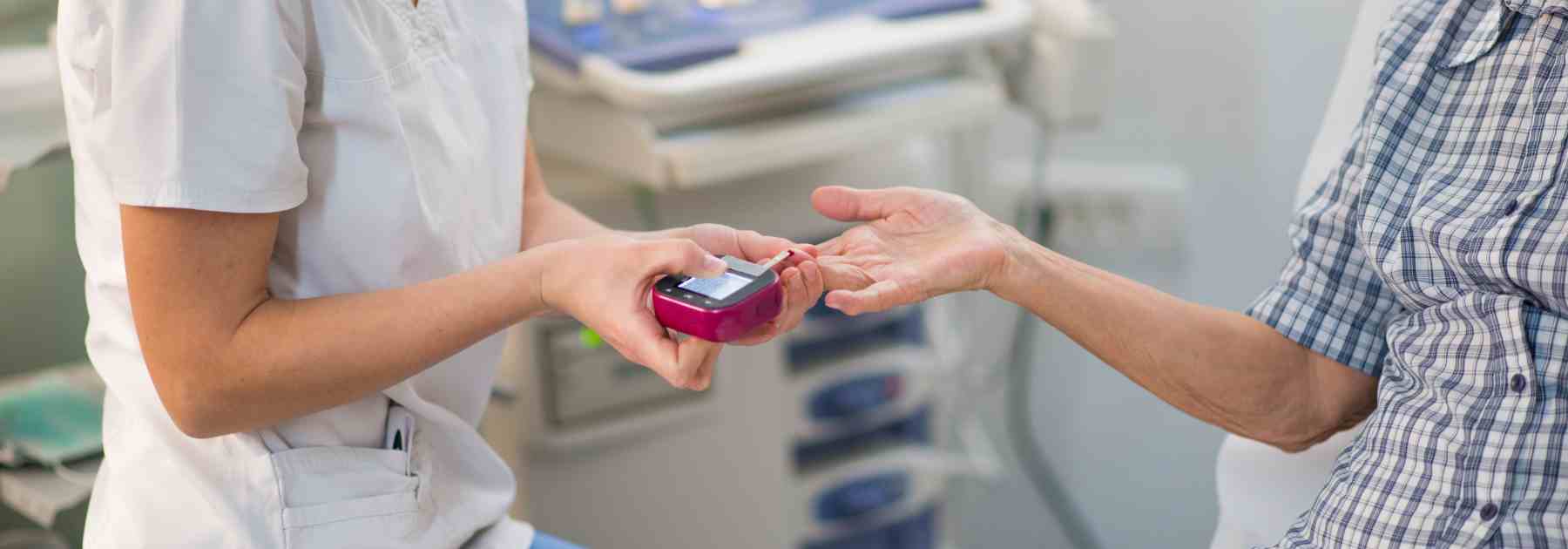

Types of Diabetes Screening Tests
There are several ways to screen for diabetes, each designed to measure your blood sugar levels and identify abnormalities:
1. HbA1c Test:
This test measures your average blood sugar levels over the past two to three months. It doesn’t require fasting and is a common diagnostic tool for Type 2 diabetes.
2, Fasting Blood Glucose Test:
Conducted after at least eight hours of fasting, this test determines your baseline blood sugar levels.
3, Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT):
This test measures how your body processes glucose. You’ll drink a sugary solution, and blood sugar levels are measured over time.
4, Random Blood Glucose Test:
A simple test that measures your blood sugar levels at any given time, regardless of when you last ate.
5. Urine Tests:
Though not definitive, urine tests can sometimes indicate high sugar levels, prompting further investigation.
The Importance of Early Diagnosis
Screening for diabetes allows for early detection, which is critical in preventing complications. If you’re identified as pre-diabetic, lifestyle interventions like improved diet, regular exercise, and weight management can often reverse the condition. For those diagnosed with diabetes, early treatment can help manage blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of long-term damage.
At G.M. Graham Pharmacy, we offer convenient and reliable diabetes screening services tailored to your needs. Our expert team is here to guide you through the process and provide personalised advice based on your results.
Take Control of Your Health Today
Diabetes screening is a simple yet powerful tool to safeguard your health. If you fall into any of the high-risk categories, don’t wait for symptoms to appear—early detection can make all the difference. Visit G.M. Graham Pharmacies to learn more about screening for diabetes and take the first step towards better health today.
This blog was written on behalf of G.M. Graham Pharmacies by Pharmacy Mentor.